Are you new to forex trading and feeling lost? Do not worry, you are not alone. Many beginners ask, “Where should I start?” The best forex trading strategies for beginners that will be given in this article can help you begin the right way.
These strategies are simple and safe. They help you avoid big losses and grow your money slowly. Even in 2025, smart steps still beat quick risks. With the right plan, even a small account can grow fast.
This guide on the best forex trading strategies for beginners gives you winning tips, one step at a time. You will learn what works and what to avoid. You will also see low-risk tactics that real traders use. These tools can help you stay calm, smart, and focused.
Let’s go in and find the best forex trading strategies for beginners that will work well for you. Yes, you specifically. This could be the start of your trading success!
What is a Forex Trading Strategy?

A forex trading strategy is a group of clear rules that guides a trader on when to start a trade, how to handle it while it’s open, and when to end it. These rules can be quite basic or extremely detailed, depending on what suits the trader best.
For traders who use technical analysis, it’s often easier to create specific entry and exit rules. However, traders who depend on fundamental analysis may find it more challenging since their decisions often involve more judgment and less strict rules.
No matter which method is used, it is very important for every trader to have a well-thought-out plan. Having a trading strategy not only builds consistency but also helps traders track and assess how well they are doing.
Top 14 Best Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners
Here are 14 simple yet powerful and best forex trading strategies for beginners that are recommended to be used by beginners:
1. Mean Reversion
Mean reversion is based on the concept that asset prices, along with other value metrics like price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios, tend to eventually return to their historical average.
This strategy relies on technical analysis tools, such as moving averages, to pinpoint assets whose recent performance significantly deviates from their typical historical trends. Traders who use mean reversion will capitalize on the asset’s price moving back toward its average.
The chart above shows favourable conditions to use mean reversion as a forex day trading strategy
2. Money Flows
The money flow indicator is used to assess whether an asset is potentially overbought or oversold by examining its trading volume and price. It works by comparing the number of trades from one day to the next to determine whether the money flow is positive or negative.
A reading above 80 typically suggests that the asset is overbought, signaling a potential sell, while a reading below 20 often indicates the asset is oversold, suggesting a buying opportunity.
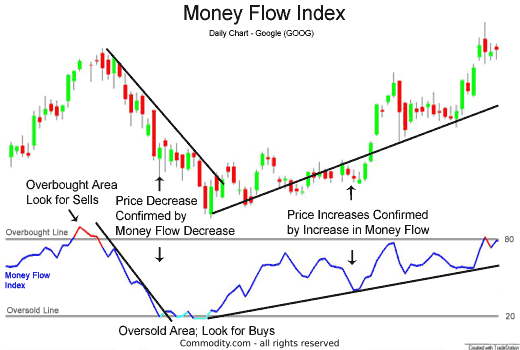
The chart above shows an example of favourable conditions to use the money flows trading strategy.
3. Trading with Price Action
Price action trading means making trading choices by closely watching the actual movement of prices, instead of heavily depending on technical tools like RSI, MACD, or Bollinger Bands. This method can involve different styles such as spotting breakouts, identifying reversals, or reading candlestick formations, whether it is basic or complex.
Usually, technical indicators are not the main part of a price action method. However, if they are used, they should only support decisions rather than lead them. For example, many traders still like using basic tools like moving averages to help understand the direction of the trend.
One of the main advantages of price action trading is that your trading chart stays neat and simple, which makes it easier to focus. Having too many indicators on the screen can lead to conflicting signals and may confuse new traders.
Understanding price movements more clearly can help you notice repeating patterns faster. This approach is especially favored by day traders, as it allows them to act quickly on short-term price changes. In fast-paced environments like day trading, a tidy chart and focus on raw price behavior make decisions easier and faster.
Below is a simple example of a breakout strategy: A trader was watching the 1.1772 level, which acted as a strong support point. The plan was to sell EUR/USD if the price dropped below that level to catch the next move downward. The larger trend was already going down, and once the breakout occurred, the price fell more than 70 pips before finding support near 1.1700.

Some traders choose to enter right at the moment the price breaks below support—sometimes even using a sell-stop order. Others prefer to wait and see how the price reacts after the breakout. Since false breakouts are common, it’s important to always follow a solid risk management plan to protect your account.
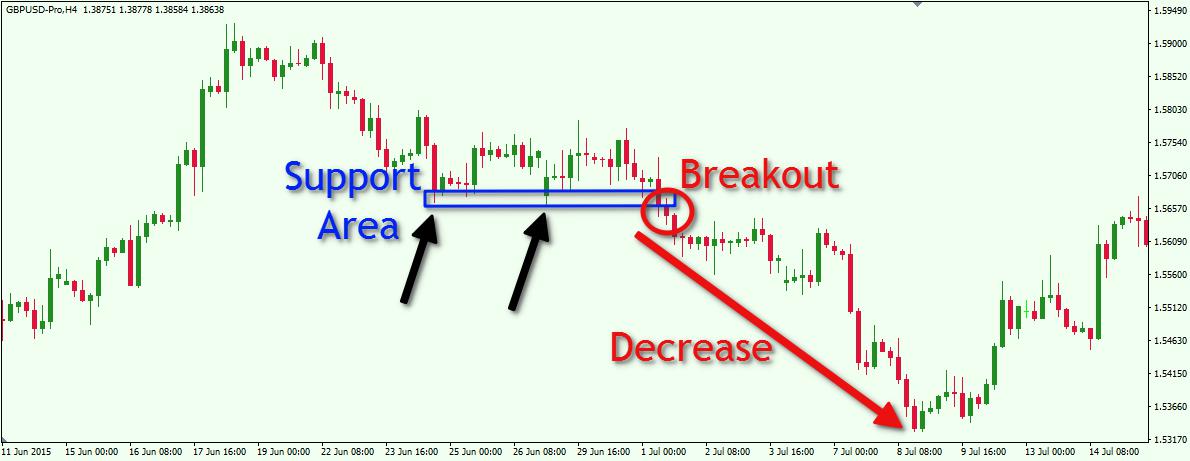
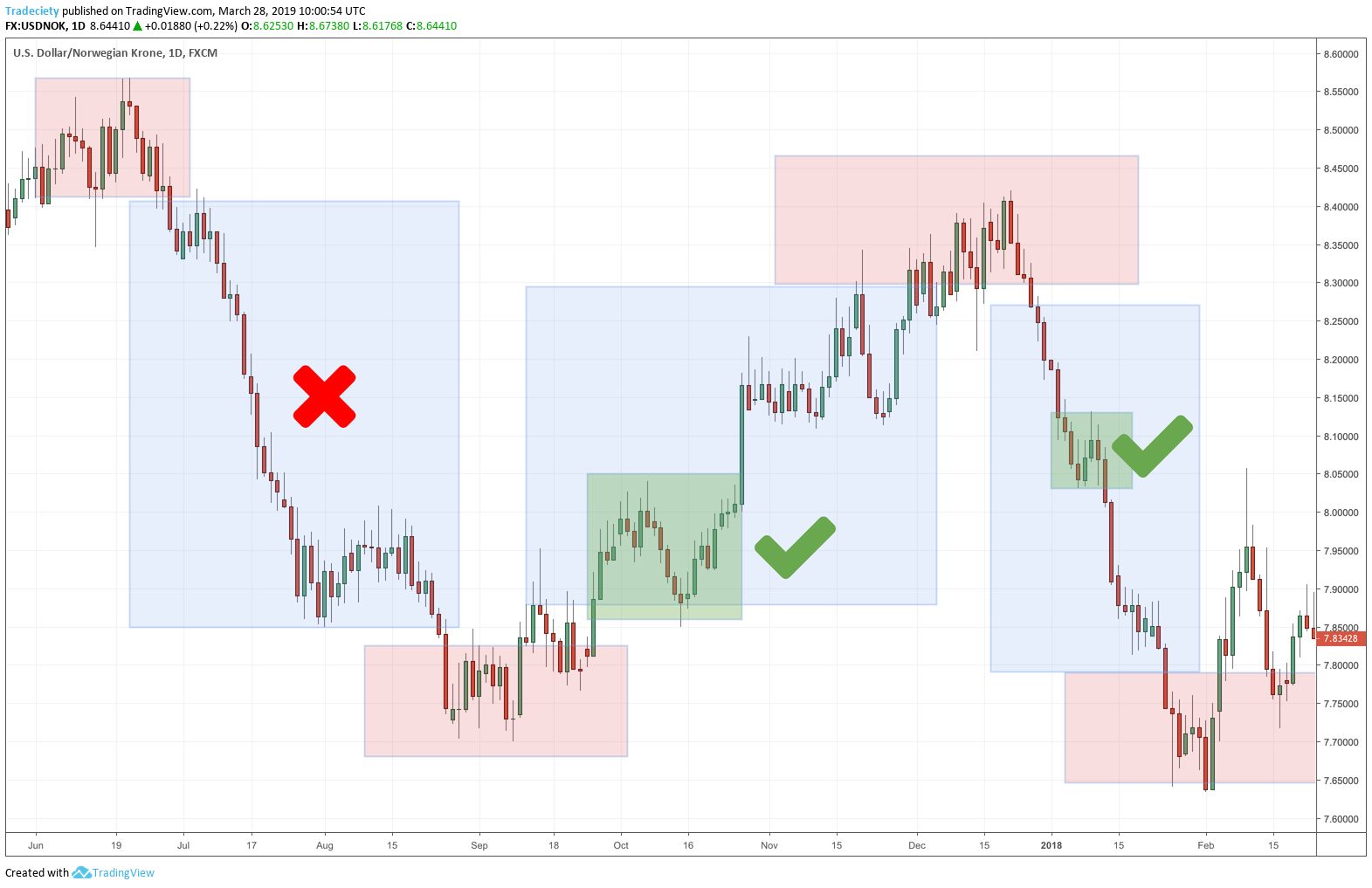
4. Range Trading Method
This method is used when a trader spots that a certain currency pair is moving within a fixed range instead of trending strongly in one direction. The size of the range depends on the chart’s timeframe and it might range from 20 pips to several hundred pips. The key is to find areas where the price keeps bouncing up from support and falling down from resistance.
To use this strategy well, traders need to find currency pairs that are not trending. One way to check this is by watching the price behavior directly. Alternatively, indicators like the average directional index (ADX) or a moving average can also help. A lower ADX reading means the market doesn’t have a strong trend.
Once you’ve picked a suitable currency pair, the next step is to mark the range where the price seems to be stuck.
The classic idea behind range trading is to sell when the price gets close to the resistance zone and to buy when it nears the support zone. While some traders focus on exact price levels, others look at a broader area.
For instance, if you spot that 1.17 is a strong resistance level, but the price often turns around before it reaches that point—say at 1.1690 or 1.1695—it might be smarter to treat the entire zone between 1.1690 and 1.17 as your sell zone. Only watching the precise level might make you miss valuable chances, as the market can turn around earlier than expected.

As an example, let’s look at EUR/SEK in the image above. This currency pair has been trading within a range. The ADX readings mostly remain low, confirming the lack of a strong trend. Also, the price has often bounced up from the 10.00/10.04 support zone and struggled to break above the 10.27–10.30 resistance zone.
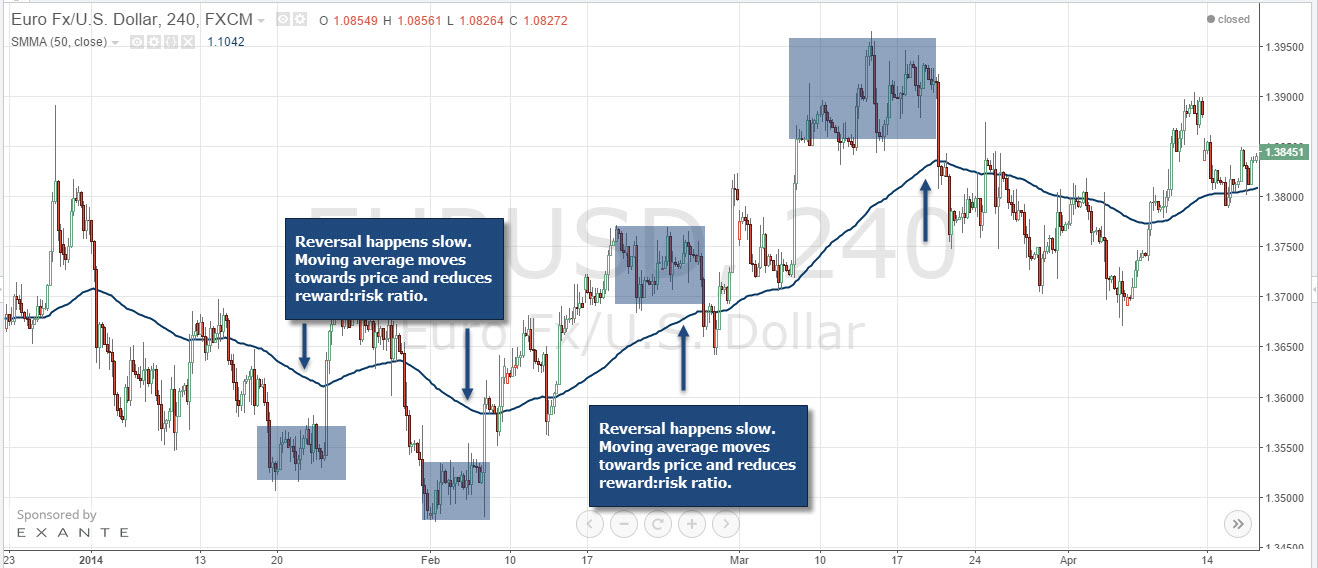
5. Trend Trading Strategy
Trend trading involves identifying opportunities that align with the current market trend. The basic principle is that the price will continue moving in the direction it is currently headed, either upwards or downwards.
When prices consistently rise (creating higher highs), the market is considered to be in an uptrend. Conversely, when prices fall (forming lower lows), it signals a downtrend.
Traders can use various tools alongside observing price action to spot trends. One widely used tool is moving averages. Traders often check if the price is positioned above or below a moving average (such as the 200-day moving average, or DMA), or look for crossover signals.
To implement moving average crossovers as entry points, a trader would use two different moving averages: a fast one and a slow one. A common setup involves using the 50-day and 200-day moving averages.
If the 50 DMA crosses above the 200 DMA, it may indicate the start of an uptrend, while the reverse crossover could signal a downtrend.

Above is an example of how this would look with the USD/JPY pair using the 50 and 200 DMA crossovers.
6. Position Trading
Position trading focuses on taking advantage of long-term trend movements, disregarding short-term market fluctuations. Traders who adopt this strategy may hold positions for weeks, months, or in some cases, years.
This method, along with scalping, is one of the most challenging trading styles. It requires great discipline to ignore daily market noise and remain composed, even when a trade moves against the trader by a significant number of pips.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/SP500IndexOffers10.4710-YearAnnualizedReturns-1a65735791464b25b67c8a8a5d3423fa.jpg)
For instance, if you had a bearish outlook on stocks in early 2018 and shorted the S&P 500 for the year, you would have benefited from the initial and year-end price drops. However, the rally from March to September could have been a tough ride. Few traders have the patience to maintain their positions for such long periods.
7. Day Trading Strategy
Day traders typically do not hold positions for just seconds, as scalpers do, but their focus is usually on specific times or trading sessions. They aim to capitalize on opportunities that arise within a trading day. While scalpers prefer using very short timeframes like the M1 chart, day traders may use charts ranging from M15 to H1.
Unlike scalpers, who might place over 10 trades daily (and some even more than 100), day traders are more selective, often aiming for 2-3 high-quality opportunities per day.

Day trading is a good fit for those who want to close positions before the end of the trading day but are not looking for the intense pressure that comes with scalping.
8. Scalping Strategy
Scalping is a trading strategy aimed at profiting from small price changes within the day. Some scalpers target only a few pips per trade, with the trades lasting from seconds to a few minutes.
Scalpers need to be quick decision-makers, adept at numbers, and able to handle the pressure of fast-paced trades. They often concentrate on specific markets (such as EUR/USD or S&P 500 futures).
The advantage of scalping lies in focusing on short-term market movements, without the worry of holding positions overnight or dealing with long-term market fundamentals.
However, scalping can be high-pressure since the trades are very brief. It requires intense focus, and the fast-paced nature of the strategy can lead to mistakes or emotional reactions. Due to this, scalping may not be the most suitable strategy for beginners.
9. Swing Trading
Swing trading refers to a trading approach where positions are typically held for several days. Traders may utilize various timeframes, such as H1 (hourly) to D1 (daily), or even weekly charts. Common strategies include trend-following, range trading, or breakout trading.
This type of trading requires patience and discipline, as it may take days before a worthwhile opportunity appears. Additionally, traders might hold onto a position for a week or more, even if they are facing an open loss. Some traders lack the patience to wait and often exit trades too early.

If you enjoy analyzing the markets at a slower pace and are comfortable with holding trades over days or even weeks, swing trading could be an ideal choice.
This style also allows for incorporating fundamental analysis, such as anticipating shifts in monetary policies or political changes, which is not feasible in faster-paced strategies like scalping.
10. Carry Trade Strategy
The carry trade strategy involves profiting from the interest rate differential between two currencies in a currency pair. Traders purchase a currency with a higher interest rate and sell one with a lower rate.
A well-known example of this is taking a long position on AUD/JPY, given Australia’s traditionally high interest rates and Japan’s low rates. This strategy results in interest payments based on the trader’s position size.
The advantage of this strategy is the potential for earning significant interest simply by holding the position. However, it is crucial to have the right market conditions for it to succeed. For example, if AUD/JPY is in a downward trend while you’re holding a long position, the interest earned will not offset the losses from the price movement.
Carry trades work best in bullish market conditions when traders are willing to take on more risk. The Japanese Yen is often seen as a safe haven, which is why many carry trades involve selling the Yen against riskier currencies.
It’s also important to consider the factors affecting the currency you are purchasing. For instance, the Australian Dollar tends to benefit from rising commodity prices, while the Canadian Dollar is closely linked to oil prices.

The chart above illustrates a period where AUD/JPY performed well, making a carry trade a viable option.
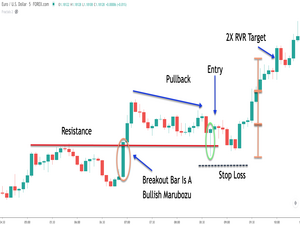
11. Breakout Strategy
A breakout strategy focuses on entering a trade once the price breaks through a certain range. Traders look for strong momentum, and the breakout itself serves as the signal to enter the trade and capitalize on the price movement that follows.
Traders may choose to enter the market immediately, requiring close monitoring of price action, or set buy-stop and sell-stop orders.
These orders are usually placed just above the previous resistance level or below the former support level. To set exit points, traders typically use classic support and resistance levels.
12. News Trading
News trading involves attempting to profit from market movements triggered by significant news events. These could include central bank meetings, economic data releases, or unexpected events like natural disasters or escalating geopolitical tensions.
This strategy can be risky, as the market becomes highly volatile during these times. Additionally, the spreads on affected instruments may widen significantly, and liquidity might decrease, increasing the risk of slippage.
Slippage occurs when a trade is executed at a much worse price than expected, or when it becomes difficult to exit the trade at the planned level.
Once you are aware of the risks, it’s essential to decide which news event you want to trade and identify the currency pair(s) most impacted. For example, a European Central Bank meeting will likely affect the Euro the most.
If you anticipate the ECB adopting a hawkish stance, signaling potential rate hikes, it might be wise to choose a low-yielding currency like the Japanese Yen. EUR/JPY could then be a suitable pair to trade.
News trading can also be approached with or without a bias. Having a bias means you have an idea of which direction the market will move based on the news event, while trading without bias means you’re open to profiting from any significant market move, regardless of direction.

The chart example above shows how the July NFP (Non-Farm Payroll) report influenced the US500.
13. Retracement Trading
Retracement trading involves temporary fluctuations in the direction of a financial instrument. It’s important to differentiate retracements from trend reversals, while reversals signal a significant shift in the overall trend, retracements are merely brief pullbacks.
When engaging in retracement trading, you are still operating in the same direction as the main trend, attempting to benefit from short-term price corrections within a dominant price movement.
There are various techniques to trade retracements. One example is using trendlines. Consider the chart of the US500 index below, which is in a clear upward trend. The rising trendline could have provided an opportunity for buying when the price touches the trendline.
Another widely used tool for retracement trading is Fibonacci retracements, particularly focusing on the 38.2%, 61.8%, and 78.6% levels.
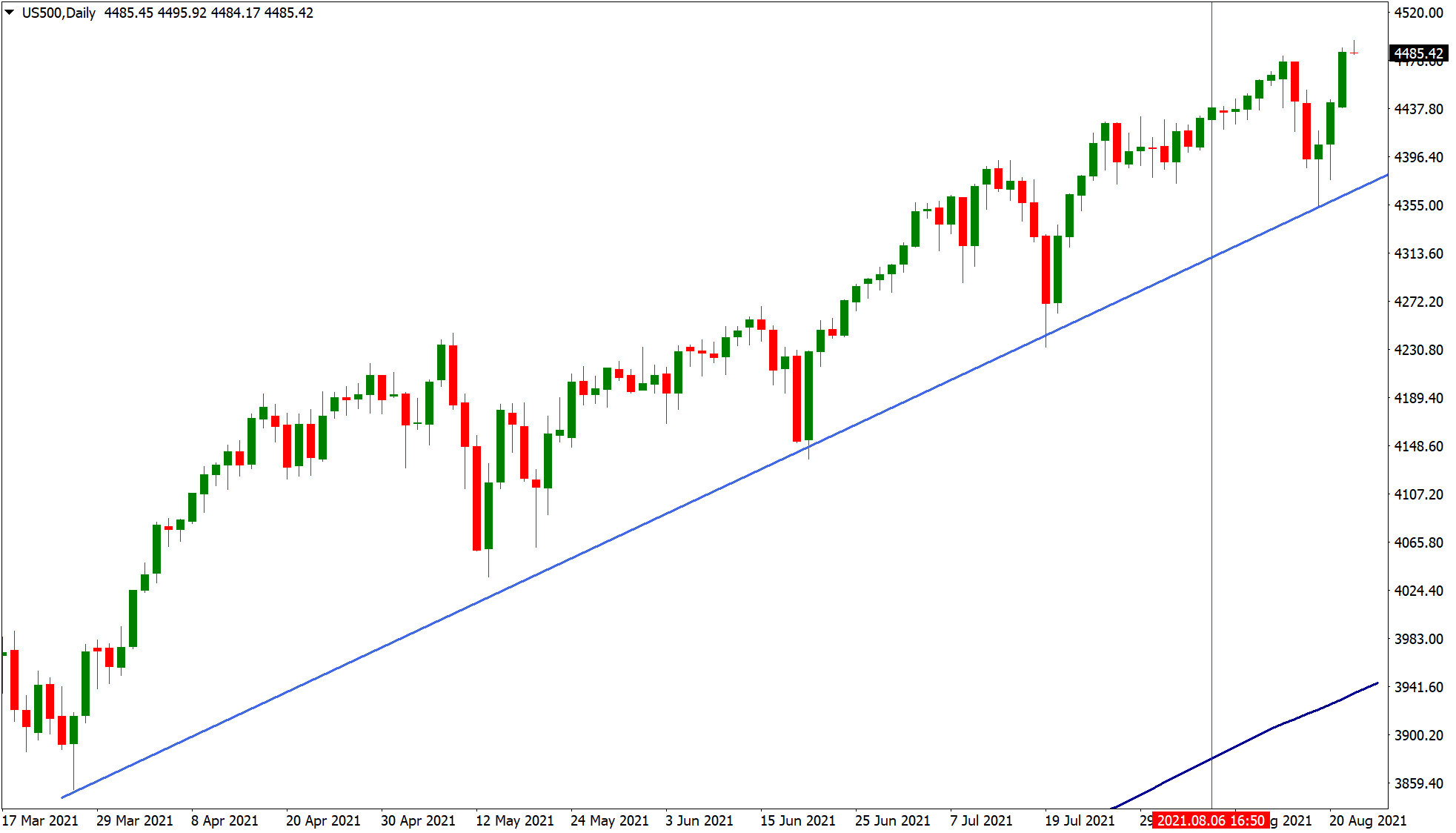
The chart above shows the US500 Retracement Trading Chart.
14. Grid Trading
Grid trading is a strategy that involves placing several orders both above and below a specific price level. The main idea is to capitalize on price fluctuations by setting buy and sell orders at consistent intervals around the target price level (for example, placing orders every 10 pips above and below).
As the price moves in one direction, your position size grows, along with your floating profit or loss. However, the risk lies in false breakouts or sudden market reversals that can impact your positions.

The trading chart above shows the AUDUSD Grid Trading Chart.
The Role of Support and Resistance in Forex Trading Strategies – What a Lot of Your Forex Mentors Won’t Tell You
Support and resistance are very important in forex trading. Many beginners do not know this at first. But these two tools can help you trade better.
So, if you are just starting out, you must learn how they work, what support is, and what resistance is. They help you make smart trading choices and avoid risky moves. Many of the best forex trading strategies for beginners are based on these levels.
So, What is Support in Forex?
Support is a price level where the market often stops falling. Think of it like a floor. When a currency pair drops to this level, buyers step in. This causes the price to bounce back up. It means traders believe the price should not go lower.

How to Use Support:
-
Buy when the price hits support and starts to rise.
-
Combine support with other tools like candlesticks or indicators.
-
Use a stop-loss below the support line to stay safe.
Example:
If EUR/USD falls to 1.0500 many times but never goes below, that is a strong support level. You can watch this zone for buying opportunities.
What is Resistance in Forex?
Resistance is the opposite of support. It is a price level where the market often stops rising. Think of it like a ceiling. When a currency pair rises to this level, sellers appear. This pushes the price back down. Traders believe the price is too high to go higher.

How to Use Resistance:
-
Sell or take profit when the price touches resistance and starts to fall.
-
Watch for reversal signs like bearish candlesticks.
-
Use a stop-loss above resistance to manage risk.
Example:
If GBP/USD often rises to 1.3000 but never breaks above, that level becomes resistance. This is where sellers are strong.
How Support and Resistance Work Together
Support and resistance often form zones. These zones create a range where price moves up and down.

Using both support and resistance, you will have the following:
In Range Trading:
-
Buy near support.
-
Sell near resistance.
-
It is simple and low-risk when done right.
In Trend Trading:
-
Support forms at higher levels in an uptrend.
-
Resistance forms lower in a downtrend.
-
Traders follow the trend using these points to enter again.
In Breakout Trading:
-
When price breaks above resistance, it may rise fast.
-
When it breaks below support, it may fall hard.
-
These breakouts often create strong new trends.
Tools to Find Support and Resistance
Here are a few ways to find support and resistance zones:
-
Horizontal lines – Draw lines at price points where the market turned in the past.
-
Moving averages – Popular ones like the 50 or 200 EMA often act like support/resistance.
-
Fibonacci retracement – This tool shows hidden support and resistance zones.
-
Round numbers – Prices like 1.0000 or 1.5000 are often strong levels.
-
Chart patterns – Double tops, bottoms, and triangles all use support and resistance.
Why Every Beginner Must Learn This
Using support and resistance can:
-
Improves your trade entries
-
Helps you set better targets
-
Keeps your losses small with smart stop-loss points
-
Makes your strategy more accurate.
That is why support and resistance are used in many of the best forex trading strategies for beginners. They are simple to learn but powerful to use.
To understand more on how support and resistance works, you can watch the video below:
How to Compare the Best Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners? – Which One is the Best for You?
Every trader should focus on identifying their own edge, which may be a specific set of skills they possess. For instance, some traders may have a quick ability to analyze numbers and thrive under the pressure of intraday trading, even if they have a short attention span.
On the other hand, a different trader might be more strategic, able to keep the broader picture in mind, and not work well under the stress of fast-paced trades.
As a beginner trader, it is especially important (very critical) to understand your personal strengths and adapt your trading strategies to suit your personality. The key is to find a strategy that works with your natural abilities, rather than forcing yourself into a strategy that doesn’t align.
Given the many advantages of forex trading, it’s up to you to compare different strategies and select the one that best fits your style.
Need more recommendations on the best forex trading strategies for beginners, you can watch this video below:
How to Pick the Best Forex Trading Strategies for Beginners
Most traders do not discover their ideal trading strategy immediately. Usually, it takes time and patience to check out and try out different methods using demo accounts or backtesting. This testing process is safe and doesn’t involve any real financial risk.
Even when a trader finally finds a strategy that seems to work well and feels comfortable, it’s rare for that same exact method to work forever. Since the forex market is always changing, traders need to keep adapting to stay effective.
If you’re new to trading, it’s usually better to begin with easy-to-follow strategies. A common mistake new traders make is adding too many indicators to their plan, which can lead to confusion and mixed messages.
Over time, you can slowly improve your strategy by using what you learn through practice, demo trading, and reviewing your past trades.
Watch the video below to see in action, one of the best forex trading strategies for beginners that is currently working:
A Word of Advice from JetxTradeAcademy
The best forex trading strategies for beginners given in this article are simple, smart, and safe. They do not need big money to begin. Any beginner can grow fast and stay safe in 2025 with patience and the right tools.
Remember to start small. Test each strategy with a demo account. Learn from your wins and losses. Also, use stop-loss tools to protect your trades. This helps keep your money safe.
Follow trusted forex news and updates. Join beginner trading forums. Watch videos that explain each method clearly. Always keep learning.
Now is the best time to begin. Pick a strategy that fits your style. Practice it well. Then go live when ready. Your trading journey starts today, with confidence and smart steps. Let success follow.
